April 6, 2025
Bladder cancer stands out not only for its incidence—around 82,000 new diagnoses in the United States each year—but also for its high cumulative cost of care. One major driver of expense is the disease’s historically high recurrence rate. Despite advances, an estimated 70–80% of patients experience a relapse within 12 months. In recent years, however, breakthroughs in both non-muscle invasive and muscle-invasive settings have begun to shift the narrative, offering potential alternatives to repeated surgeries and hospital visits.
Understanding NMIBC vs. MIBC
Bladder cancer is broadly divided into non-muscle invasive (NMIBC) and muscle-invasive (MIBC) disease. NMIBC, which accounts for roughly 75% of newly diagnosed bladder cancers, typically remains confined to the bladder lining. Although less immediately aggressive, it often comes back after first-line treatments, requiring repeated procedures and close monitoring. Meanwhile, MIBC—about 25% of new cases—can quickly spread deeper into the bladder wall and beyond, posing a higher risk for systemic metastases. Because of this distinct risk profile, MIBC is generally managed more aggressively from the outset.
Who Is Affected?
The median age at diagnosis tends to be in the 60s or 70s. Smoking is the most significant risk factor, followed by chronic bladder irritation and certain genetic predispositions. Persistent infections may also contribute. Recognizing and reducing these risk factors remains a critical piece of any long-term strategy to lower bladder cancer incidence.
Standard of Care Breakdown
Treatment for NMIBC typically starts with transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT). After resection, intravesical therapy—most often BCG or chemotherapy—is introduced to destroy microscopic disease and reduce relapse. However, patients who fail BCG or are deemed at high risk can face a radical cystectomy if there are no effective bladder-sparing alternatives.
For MIBC, the standard approach involves radical cystectomy in combination with cisplatin-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy, aiming to address both the primary tumor and any micrometastatic disease. In patients who are cisplatin-ineligible or who decline surgery, a chemoradiation regimen can be considered as a curative-intent option. Despite these measures, recurrence rates remain stubbornly high, spurring the development of new approaches in both NMIBC and MIBC.
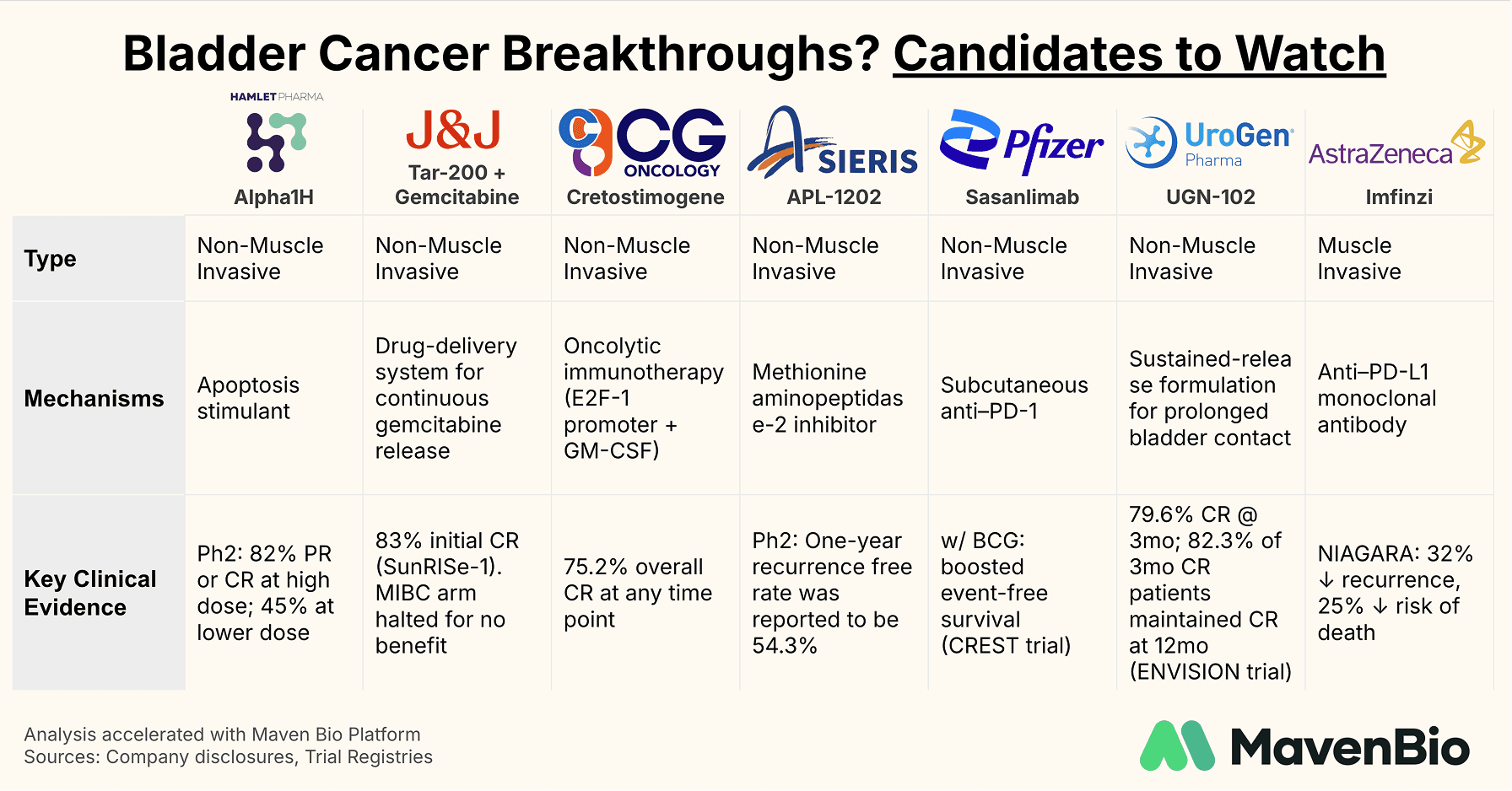
Key Therapeutics in Development
NMIBC: UGN-102 (UroGen) One of the more prominent emerging therapies for NMIBC is UGN-102, a mitomycin formulation delivered via a temperature-responsive gel that solidifies in the bladder. In the Phase 3 ENVISION trial, 79.6% of patients achieved a complete response at three months, and 82.3% of those responders remained in remission at the 12-month mark. The advantage over conventional mitomycin arises from the gel’s ability to prolong drug contact time with tumor cells, which could spare many patients repeated surgeries for low-grade, recurrent tumors.
NMIBC: Sasanlimab (Pfizer)
Sasanlimab is a subcutaneous anti–PD-1 antibody that showed promising results when combined with BCG in Pfizer’s Phase 3 CREST trial. The addition of sasanlimab significantly improved event-free survival compared to BCG alone in high-risk NMIBC. Early trials also point to potential utility in muscle-invasive disease for patients who are ineligible for cisplatin, although Pfizer’s main focus has shifted to the BCG-naïve setting, where this drug could make first-line immunotherapy more accessible.
NMIBC: TAR-200 (Johnson & Johnson)
TAR-200 exemplifies an evolving approach to drug delivery. Rather than standard instillations, it uses a gemcitabine-releasing intravesical device, which remains in the bladder to provide sustained chemotherapy exposure. In the Phase 2b SunRISe-1 trial for high-risk, BCG-unresponsive NMIBC, TAR-200 achieved an 83% complete response rate—a remarkable outcome in this difficult-to-treat population. Johnson & Johnson has applied for approval based on these data. However, the SunRISe-2 arm in MIBC was halted because TAR-200 did not improve outcomes over standard chemoradiation, illustrating how a therapy can excel in NMIBC but face challenges in more advanced disease.
MIBC: Imfinzi (AstraZeneca)
For muscle-invasive bladder cancer, AstraZeneca’s Imfinzi (durvalumab) has captured attention in the NIAGARA trial by combining immunotherapy and chemotherapy prior to radical cystectomy, followed by durvalumab monotherapy. The trial demonstrated a 32% reduction in disease recurrence and a 25% drop in mortality risk relative to chemotherapy alone, positioning Imfinzi as a potential new backbone of perioperative care. The FDA has granted Priority Review with a target decision date (PDUFA) in the second quarter of 2025. If approved, this regimen may become a key component of managing MIBC, possibly improving both survival and long-term disease control.
Final Take
Bladder cancer has long been known for frequent relapses, driving high treatment costs and diminishing patient quality of life. Yet the landscape is evolving. Innovative delivery platforms like UGN-102 and TAR-200 illustrate the power of rethinking how drugs contact the bladder. Meanwhile, novel immunotherapies—subcutaneous PD-1 inhibitors like sasanlimab or perioperative PD-L1 blockade with Imfinzi—promise to deepen and prolong responses across both NMIBC and MIBC. Although no single breakthrough will eliminate the high recurrence rates overnight, these advances may significantly move the needle for patients who stand to benefit from reduced surgical interventions and longer remissions. For many clinicians and researchers, this moment marks a long-awaited turning point in tackling one of the most persistent challenges in oncology.





